For better experience switch to desktop



Domino’s Location & Address
Domino’s Location & Address
Domino's, India's top QSR conglomerate, faced issues such as incorrect orders and delivery riders grappling with inaccurate or undeliverable addresses. This case study delves into identifying and solving these problems at the root cause, aiming to enhance the overall ordering process efficiency.
Domino's, India's top QSR conglomerate, faced issues such as incorrect orders and delivery riders grappling with inaccurate or undeliverable addresses. This case study delves into identifying and solving these problems at the root cause, aiming to enhance the overall ordering process efficiency.
Situation
Domino's encountered friction in their ordering process due to challenges related to location detection, selection, and delivery, leading to an increase in bad orders.
task
Enhance the user experience of Domino's app by addressing location and address related challenges and improving the overall journey.
action
Implemented smart location detection
Improved address input, reduced manual efforts
Encouraged takeaway orders
Offered discounts for takeaway to promote convenience.
result
New users' location improvement enabled a 20.30% uplift in overall conversion.
46.5% uplift in conversion (6.54% → 9.58%) for store pickup and non-deliverable areas.
A significant drop in bad orders.
THE PROBLEM
Addressing order accuracy
Addressing order accuracy
Domino's encountered challenges with their ordering system, particularly related to location detection, selection, and delivery. These challenges resulted in an increase in bad orders and a decrease in overall user satisfaction. The goal was to address these challenges and improve the user experience to reduce bad orders and enhance satisfaction levels.
Domino's encountered challenges with their ordering system, particularly related to location detection, selection, and delivery. These challenges resulted in an increase in bad orders and a decrease in overall user satisfaction. The goal was to address these challenges and improve the user experience to reduce bad orders and enhance satisfaction levels.
why is it important
Negative impact of bad orders on efficiency, satisfaction, and profitability
Negative impact of bad orders on efficiency, satisfaction, and profitability
Root causes of bad orders:
Root causes of bad orders:
System inefficiencies in detecting customer locations
Inadequate or absent nudges
No aide in decision-making
System inefficiencies in detecting customer locations
Inadequate or absent nudges
No aide in decision-making
Consequences:
Consequences:
Inaccurate orders
Customer discontent
Operational challenges
High return on order and unnecessary additional costs
Inaccurate orders
Customer discontent
Operational challenges
High return on order and unnecessary additional costs
Pivotal actions:
Pivotal actions:
Addressing root causes
Mitigating the impact of bad orders
Enhancing customer satisfaction
Streamlining operations
Addressing root causes
Mitigating the impact of bad orders
Enhancing customer satisfaction
Streamlining operations
the challenge
How might we reduce bad orders and enhance operational efficiency?
How might we reduce bad orders and enhance operational efficiency?
In alignment with our primary goal, we undertook the identification of issues within the existing user experience, funnel analysis, understanding of store SOPs, and technical constraints. Within this expansive scope, we encountered specific challenges that demanded attention:
Problem 1 – 34% loss of new users during onboarding: We meticulously addressed the onboarding process to minimise the significant 34% loss of new users, implementing strategic measures to enhance user engagement and retention.
Problem 2 – 25% drop-off during choosing/modifying address: Recognising the critical stage of address selection, we implemented targeted improvements to reduce the substantial 25% drop-off rate, ensuring a smoother user journey.
Problem 3 – Address entry challenges: Users resorting to unconventional address entries due to permissible character limits prompted us to optimise the address input interface, refining it to accommodate user preferences without compromising accuracy. E.g: 3rd Floor, Mahajan Niwas, Opposite R K Public School, Dwarka Sec-B, Delhi would be written as 3 Flr, Mahajan Niwas, RK Pub. School, Dwarka
Problem 4 – Map interface challenges: Resolving issues related to irrelevant zoom levels and refining mental models within the map interface, we elevated the user experience by aligning it more closely with user expectations.
Problem 5 – Opportunity loss for non-deliverable customers: Recognising the potential in non-deliverable customer segments, constituting approximately 17% of users who choose delivery but fall outside the delivery zone, we implemented targeted strategies to capture this opportunity effectively.
In alignment with our primary goal, we undertook the identification of issues within the existing user experience, funnel analysis, understanding of store SOPs, and technical constraints. Within this expansive scope, we encountered specific challenges that demanded attention:
Problem 1 – 34% loss of new users during onboarding: We meticulously addressed the onboarding process to minimise the significant 34% loss of new users, implementing strategic measures to enhance user engagement and retention.
Problem 2 – 25% drop-off during choosing/modifying address: Recognising the critical stage of address selection, we implemented targeted improvements to reduce the substantial 25% drop-off rate, ensuring a smoother user journey.
Problem 3 – Address entry challenges: Users resorting to unconventional address entries due to permissible character limits prompted us to optimise the address input interface, refining it to accommodate user preferences without compromising accuracy. E.g: 3rd Floor, Mahajan Niwas, Opposite R K Public School, Dwarka Sec-B, Delhi would be written as 3 Flr, Mahajan Niwas, RK Pub. School, Dwarka
Problem 4 – Map interface challenges: Resolving issues related to irrelevant zoom levels and refining mental models within the map interface, we elevated the user experience by aligning it more closely with user expectations.
Problem 5 – Opportunity loss for non-deliverable customers: Recognising the potential in non-deliverable customer segments, constituting approximately 17% of users who choose delivery but fall outside the delivery zone, we implemented targeted strategies to capture this opportunity effectively.
my role
As the Head of Design, my role encompassed strategic planning for an optimal user experience, stakeholder management, defining the project's scope and roadmap, resource planning, and tracking key metrics. Leading a diverse team that included a lead designer, junior product designer, UX researcher collaborating with product manager, front-end engineer, and backend engineers, I played a pivotal role in orchestrating a collaborative and effective design process.
As the Head of Design, my role encompassed strategic planning for an optimal user experience, stakeholder management, defining the project's scope and roadmap, resource planning, and tracking key metrics. Leading a diverse team that included a lead designer, junior product designer, UX researcher collaborating with product manager, front-end engineer, and backend engineers, I played a pivotal role in orchestrating a collaborative and effective design process.
the team
Lead Designer
Lead Designer
Junior Product Designer
Junior Product Designer
UX Researcher
UX Researcher
Product Manager
Product Manager
Front-end Engineer
Front-end Engineer
Backend Engineers
Backend Engineers
Operations Team
Operations Team
Recruiting Agency
Recruiting Agency
The Process
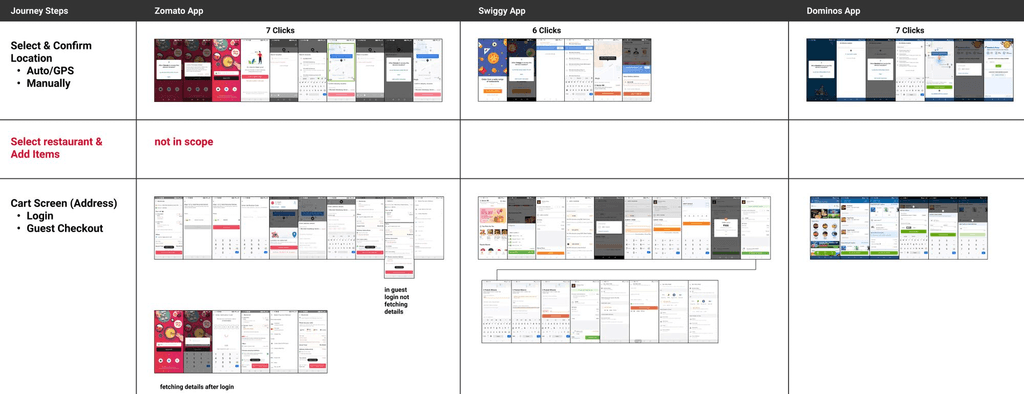
Competitive analysis
Competitive analysis
We conducted a comparative analysis of the onboarding to delivery experience across Swiggy and Zomato, two leading players in the food delivery industry. This comprehensive review allowed us to discern industry trends, technologies, features, strengths, and weaknesses. This informed our product strategy for staying competitive in the market.
We conducted a comparative analysis of the onboarding to delivery experience across Swiggy and Zomato, two leading players in the food delivery industry. This comprehensive review allowed us to discern industry trends, technologies, features, strengths, and weaknesses. This informed our product strategy for staying competitive in the market.

User persona
User persona
We crafted a user persona to understand and empathise with the end users of our product or service. By creating a detailed profile like Priya Patel, we gained insight into the needs, preferences, pain points, and motivations of our target audience. This allowed us to tailor our product or service to meet the specific requirements of users like Priya, resulting in a more effective and impactful solution.
We crafted a user persona to understand and empathise with the end users of our product or service. By creating a detailed profile like Priya Patel, we gained insight into the needs, preferences, pain points, and motivations of our target audience. This allowed us to tailor our product or service to meet the specific requirements of users like Priya, resulting in a more effective and impactful solution.


User interviews & usability test
User interviews & usability test
Usability testing and in-depth interviews were pivotal in refining our product's user experience. Through usability tests, we observed user interactions to identify and address interface issues, ensuring intuitive navigation and user satisfaction. In-depth interviews provided deeper insights into user needs and behaviours, guiding us in tailoring our product to better serve our audience. Together, these methodologies facilitated an iterative design process, resulting in a user-centric solution that meets the expectations of our users.

Proposal Document
for Research Study
User voice
"I found a workaround since there's no home delivery available. I just put an address at the street corner, then go and collect the order myself."
"I found a workaround since there's no home delivery available. I just put an address at the street corner, then go and collect the order myself."
identified issues
Issues in onboarding flow (led to 34% drop-off)
5 steps in happy flow, 9 steps in a non-happy flow
5 steps in happy flow, 9 steps in a non-happy flow
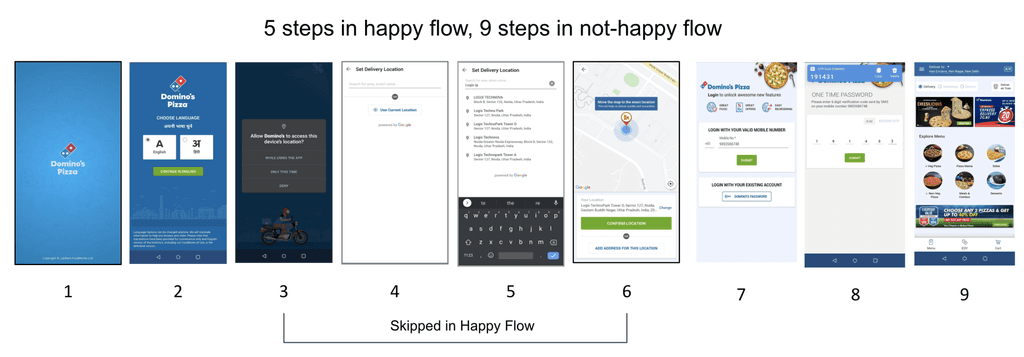

Friction caused by multiple screens: In a non-happy flow, it took 9 steps to reach the homepage, causing significant friction for users navigating through multiple screens.
Limited usefulness of mandatory steps: Mandatory steps, such as language selection, have proven useful for only a limited set of users.
Massive drop due to exact location detection: Exact location detection prior to the homepage has led to a significant drop in user engagement.
Manual entry requirement for location: Users have been required to manually enter their location if GPS fails to fetch it, even before reaching the homepage.
Character limit restriction: Users have faced constraints due to character limit restrictions.
Redundant address input: Despite GPS detecting the location or society, users have been required to input the entire address.
Friction caused by multiple screens: In a non-happy flow, it took 9 steps to reach the homepage, causing significant friction for users navigating through multiple screens.
Limited usefulness of mandatory steps: Mandatory steps, such as language selection, have proven useful for only a limited set of users.
Massive drop due to exact location detection: Exact location detection prior to the homepage has led to a significant drop in user engagement.
Manual entry requirement for location: Users have been required to manually enter their location if GPS fails to fetch it, even before reaching the homepage.
Character limit restriction: Users have faced constraints due to character limit restrictions.
Redundant address input: Despite GPS detecting the location or society, users have been required to input the entire address.
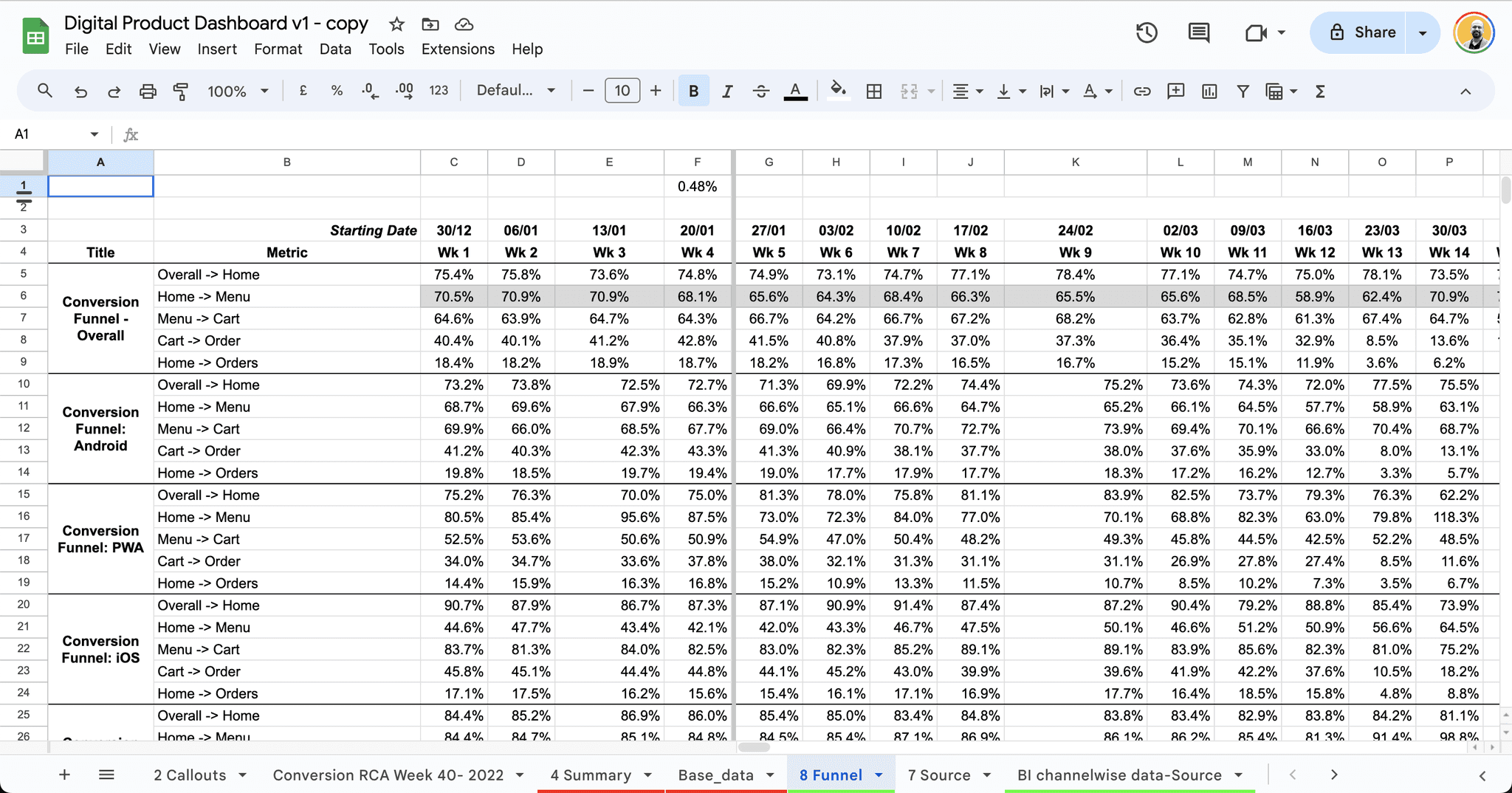
Funnel analysis
Funnel analysis

Design iterations
Design iterations
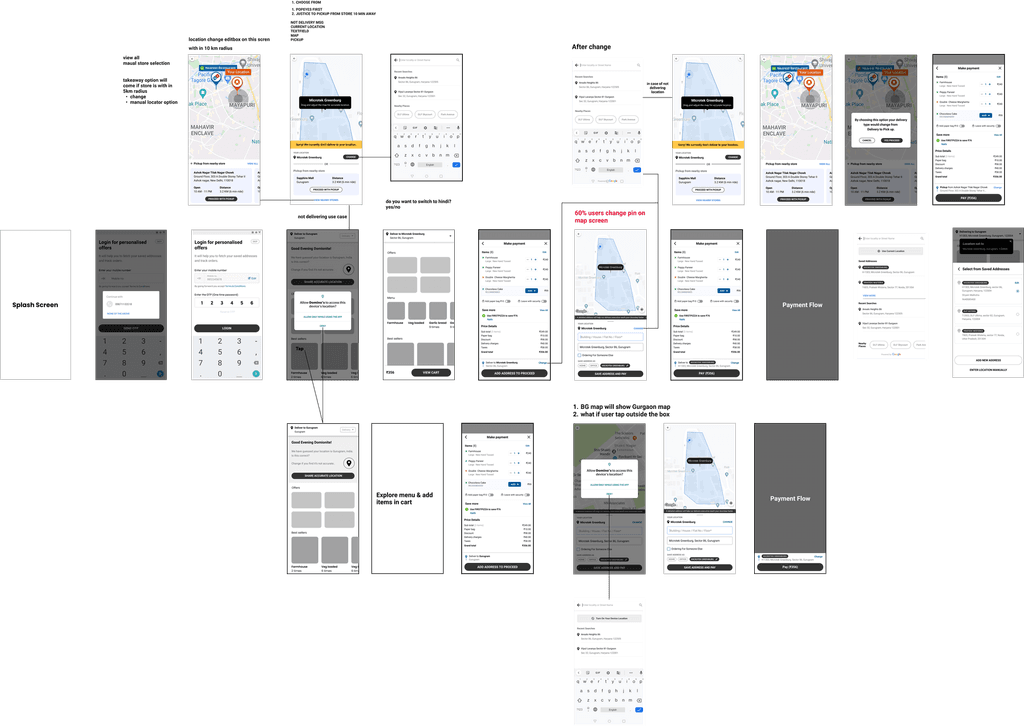

Scope and Constraints
Trade-offs in Location Detection
Trade-offs in Location Detection
Boundary creation:
Boundary creation:
Trade-offs between in-house development and outsourcing for boundary creation.
Considerations include cost, expertise, and time constraints.
Trade-offs between in-house development and outsourcing for boundary creation.
Considerations include cost, expertise, and time constraints.
Price point for GPS ping:
Price point for GPS ping:
Determine the cost associated with each GPS ping for accurate location detection.
Evaluate affordability for users while ensuring profitability for the business.
Determine the cost associated with each GPS ping for accurate location detection.
Evaluate affordability for users while ensuring profitability for the business.
IP inaccuracy:
IP inaccuracy:
Acknowledge the constraint of IP inaccuracy within a radius of up to 50 kilometres.
Explore mitigation strategies such as refining algorithms or incorporating alternative location detection methods.
Acknowledge the constraint of IP inaccuracy within a radius of up to 50 kilometres.
Explore mitigation strategies such as refining algorithms or incorporating alternative location detection methods.
Additional pricing for Google maps:
Additional pricing for Google maps:
Assess the feasibility of integrating Google Maps for advanced UI features.
Determine the additional cost incurred and weigh it against the value it adds to the user experience.
Assess the feasibility of integrating Google Maps for advanced UI features.
Determine the additional cost incurred and weigh it against the value it adds to the user experience.
Resource allocation:
Resource allocation:
Allocate resources effectively to address scope requirements while adhering to budget constraints.
Prioritise features based on user needs and business objectives to optimise resource utilisation.
Allocate resources effectively to address scope requirements while adhering to budget constraints.
Prioritise features based on user needs and business objectives to optimise resource utilisation.
Risk management:
Risk management:
Identify potential risks associated with scope and constraints, such as technical limitations or budget overruns.
Develop mitigation plans to address these risks and minimise their impact on project delivery.
Identify potential risks associated with scope and constraints, such as technical limitations or budget overruns.
Develop mitigation plans to address these risks and minimise their impact on project delivery.
Compliance and legal considerations:
Compliance and legal considerations:
Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and legal requirements related to location tracking and user data.
Factor in any regulatory constraints that may impact the implementation of certain features or functionalities.
Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and legal requirements related to location tracking and user data.
Factor in any regulatory constraints that may impact the implementation of certain features or functionalities.
The solution
Onboarding-to-Home
Onboarding-to-Home
With zip-zap-zoom philosophy at centre: We effectively streamlined the entire onboarding process into a seamless one-click journey.
Nudges for decision making: Strategic nudges were implemented to reduce cognitive overload and simplify decision-making for users.
Leveraging multiple touchpoints: The system now relies on various touchpoints, including GPS, IP detection, manual location input, and boundary selection to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, it facilitated menu customisation based on IP/GPS data.
Minute-level experience enhancement: By focusing on minute details, we have elevated the user experience, leading to a significant improvement in the overall ordering process for Domino's customers.
With zip-zap-zoom philosophy at centre: We effectively streamlined the entire onboarding process into a seamless one-click journey.
Nudges for decision making: Strategic nudges were implemented to reduce cognitive overload and simplify decision-making for users.
Leveraging multiple touchpoints: The system now relies on various touchpoints, including GPS, IP detection, manual location input, and boundary selection to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, it facilitated menu customisation based on IP/GPS data.
Minute-level experience enhancement: By focusing on minute details, we have elevated the user experience, leading to a significant improvement in the overall ordering process for Domino's customers.
Eliminate onboarding dead-ends: Smart pick-up nudge
Eliminate onboarding dead-ends: Smart pick-up nudge
Smart nudge to takeaway (pickup from store): Smart location detection nudges users to opt for takeaway seamlessly, ensuring a smoother ordering experience without dead ends. This enhancement significantly improved order fulfilment speed and reduced delivery overhead. It also displays the nearest store with distance and estimated time to reach, encouraging takeaway.
Effective discounting for pickup efforts: Offered enticing discounts for takeaway orders to incentivise users and promote the convenience of picking up orders from the nearest store. An appropriate apologetic copy is provided as needed.
Reduced cognitive load: Simplified store selection and identifying the nearest store, reducing cognitive load for users and enhancing overall order placement experience. Additionally, it shows the nearest store with distance and estimated time to reach, aiding decision-making.
Smart nudge to takeaway (pickup from store): Smart location detection nudges users to opt for takeaway seamlessly, ensuring a smoother ordering experience without dead ends. This enhancement significantly improved order fulfilment speed and reduced delivery overhead. It also displays the nearest store with distance and estimated time to reach, encouraging takeaway.
Effective discounting for pickup efforts: Offered enticing discounts for takeaway orders to incentivise users and promote the convenience of picking up orders from the nearest store. An appropriate apologetic copy is provided as needed.
Reduced cognitive load: Simplified store selection and identifying the nearest store, reducing cognitive load for users and enhancing overall order placement experience. Additionally, it shows the nearest store with distance and estimated time to reach, aiding decision-making.
Other Improvements
Other Improvements
Promoted GPS usage: Encouraged users to utilise GPS for address input.
Displayed nearby landmarks: Showed nearby landmarks for enhanced location identification.
Improved search results: Provided better search results for increased accuracy, including merged and sorted results by distance.
Integrated saved addresses: Incorporated saved addresses into search results and enabled recent searches for convenience.
Simplified address entry: Enabled one-step entry with prefilled location/society and increased address length.
Unified contact information: Eliminated separate steps for entering contact details, facilitating seamless order placement.
Enhanced ordering experience: Utilised visual cues, local boundaries, and precise pointer pin for faster selections and a clearer UI. Improved zoom levels and introduced a new-age UI for readability.
Facilitated ordering for others: Enabled easy ordering for someone else with specific contact information and stored guest details for future recall.
Optimised conversion for non-GPS users: Enhanced conversion for non-GPS users by optimising the manual locator funnel and implementing IP-based location detection for contextual menus.
Promoted GPS usage: Encouraged users to utilise GPS for address input.
Displayed nearby landmarks: Showed nearby landmarks for enhanced location identification.
Improved search results: Provided better search results for increased accuracy, including merged and sorted results by distance.
Integrated saved addresses: Incorporated saved addresses into search results and enabled recent searches for convenience.
Simplified address entry: Enabled one-step entry with prefilled location/society and increased address length.
Unified contact information: Eliminated separate steps for entering contact details, facilitating seamless order placement.
Enhanced ordering experience: Utilised visual cues, local boundaries, and precise pointer pin for faster selections and a clearer UI. Improved zoom levels and introduced a new-age UI for readability.
Facilitated ordering for others: Enabled easy ordering for someone else with specific contact information and stored guest details for future recall.
Optimised conversion for non-GPS users: Enhanced conversion for non-GPS users by optimising the manual locator funnel and implementing IP-based location detection for contextual menus.
One click address input
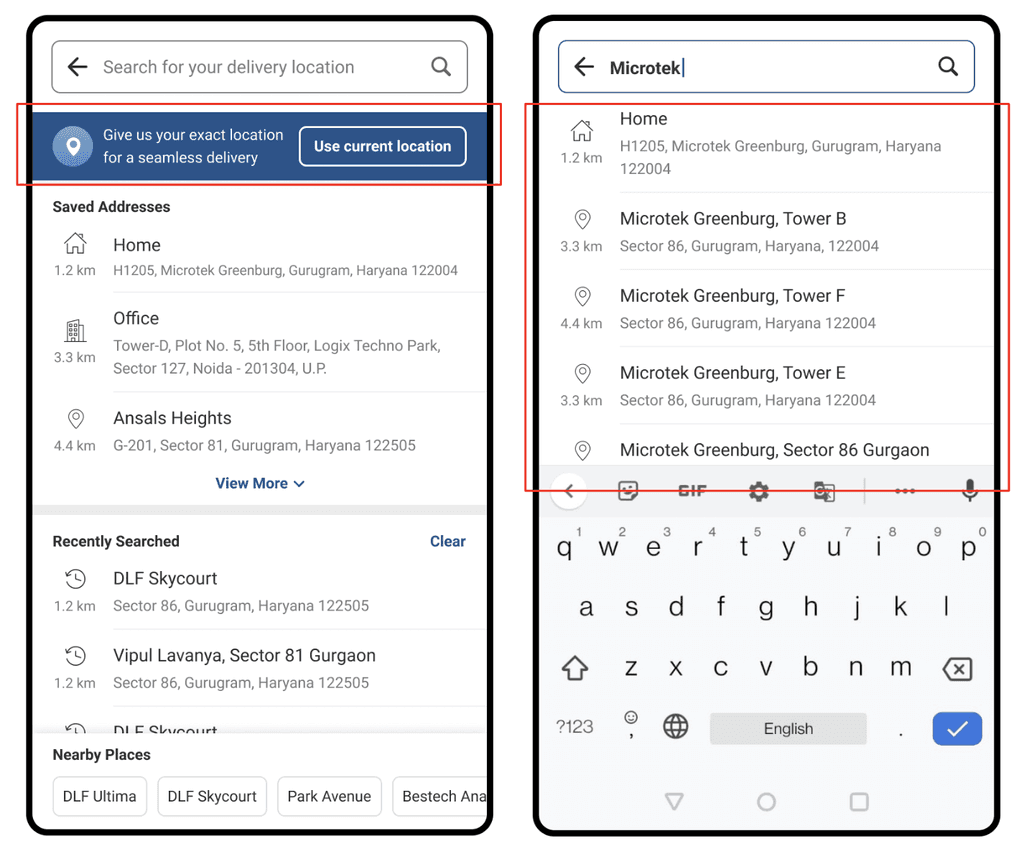

Comprehensive location search (L) ordered search results (R)
Tag editing
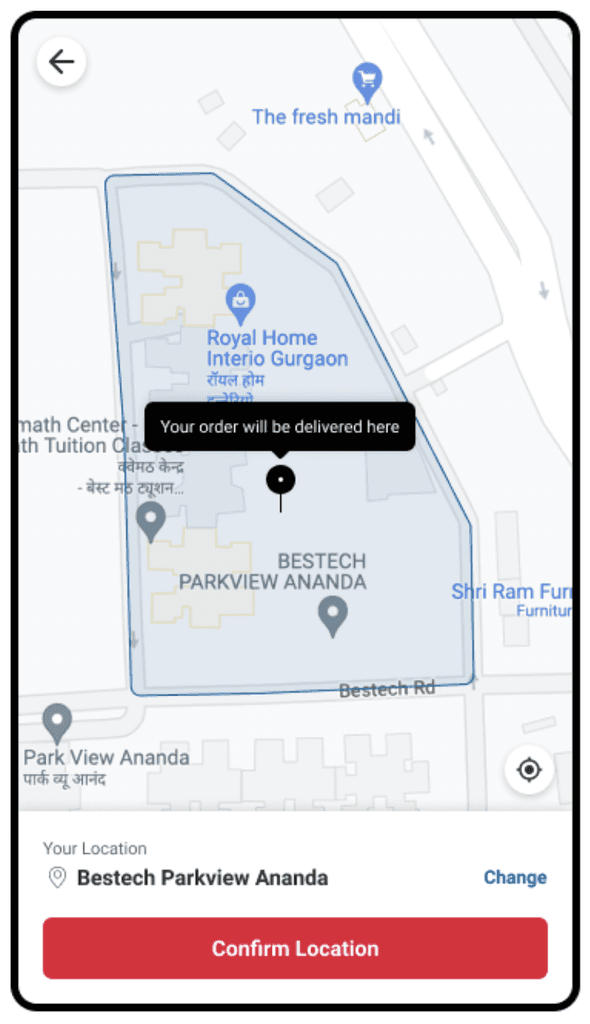
Highlighted area boundaries
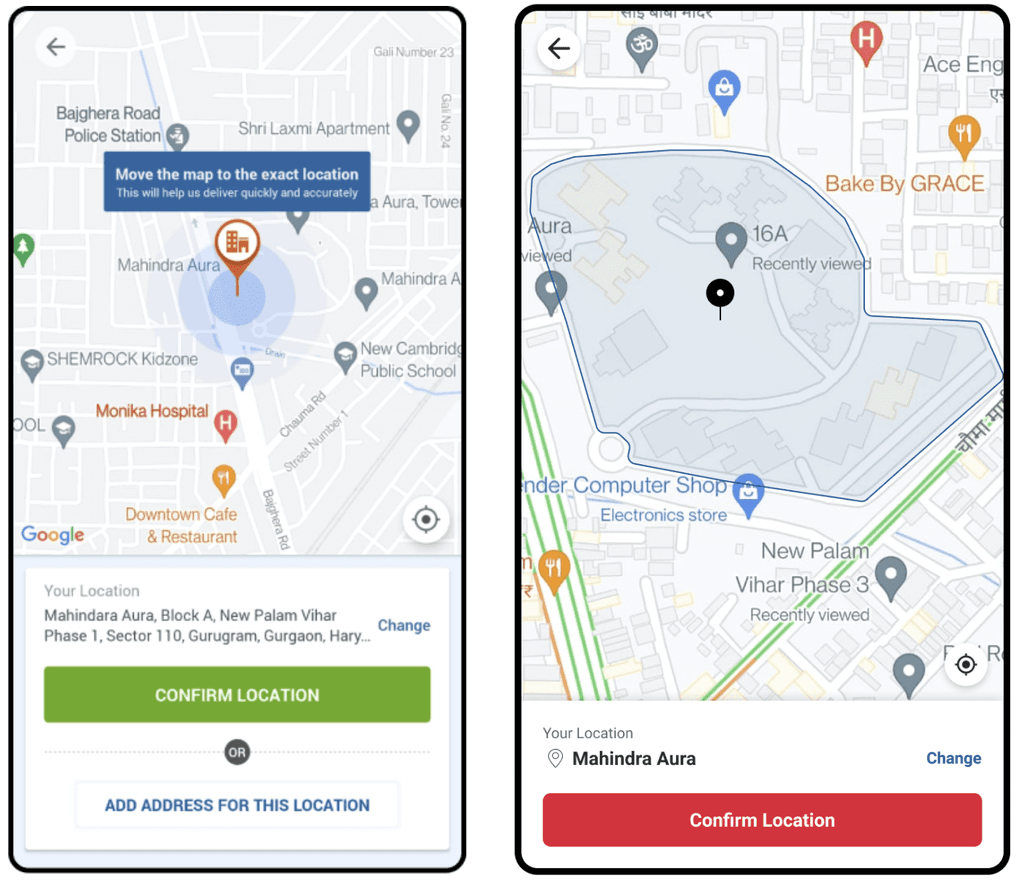

Rich map interface (before and after)
Ordering for someone else
The result
Result and Takeaway
Result and Takeaway
Since the implementation of Domino's revamped location features, we have observed a notable reduction in customer complaints related to delivery accuracy and address input issues. Moreover, users have provided positive feedback on the streamlined process of configuring their delivery locations, resulting in significant time savings. From this experience, we've learned the importance of prioritising user-centric design in addressing challenges such as GPS accuracy, boundary creation, and integration with Google Maps. By focusing on enhancing the user experience and simplifying configuration processes, we can effectively improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Since the implementation of Domino's revamped location features, we have observed a notable reduction in customer complaints related to delivery accuracy and address input issues. Moreover, users have provided positive feedback on the streamlined process of configuring their delivery locations, resulting in significant time savings. From this experience, we've learned the importance of prioritising user-centric design in addressing challenges such as GPS accuracy, boundary creation, and integration with Google Maps. By focusing on enhancing the user experience and simplifying configuration processes, we can effectively improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
New users' location improvement enabled a 20.30% uplift in conversion.
46.5% uplift in conversion (6.54% → 9.58%) for Store Pickup and non-deliverable areas.
A significant drop in bad orders.
New users' location improvement enabled a 20.30% uplift in conversion.
46.5% uplift in conversion (6.54% → 9.58%) for Store Pickup and non-deliverable areas.
A significant drop in bad orders.
–––––––––––––––––––
Thank You! 😊
–––––––––––––––––––
Thank You! 😊
Get in touch
Always open to meaningful conversations around design leadership, product strategy, and scaling teams.
